What is data archiving?
Our datacenter does not allow data archiving, use the server for file storage or mail storage, only actual messages should be located there. Storing old emails is equal to file/data archiving. As result accounts with old emails are in size dramatically and occupy disk space excessively. That creates critical issues for server performance and backup system on unlimited hosting servers.
NOTE: This is the customer’s responsibility to take regular backups to avoid any inconvenience. Our datacenter conducts weekly disaster recovery backup of the server and charge an amount for the restoration of any cpanel backup if available. Furthermore, datacenter does not take backup of those accounts which are consuming more than 20GB.
What do you mean by Unlimited Hosting? (unlimited disk space and bandwidth)?
The datacenter does not set limits on the disk space and bandwidth (data transfer) that we provide in plans that are marked “Unlimited” as infinity (∞). We want you to have the resources available to you to build a great online presence. Even though we want you to succeed, we need to ensure that we’re providing all of our customers with optimum service. As such we do require all of our customers to be fully compliant with our Excessive Resource User Policy/Terms of Service and utilize disk space and bandwidth related to normal operation of a personal or small business website.
Storage of Backups and Mail
You may not use your hosting account as a backup solution or to host archived mail. Archived mail is defined as messages older than thirty (30) days or emails totaling ten (10) gigabytes or larger. Our Services are designed to host active website data only and may not be used as a data repository. Computer Xperts reserves the right to remove backups and/or archives from your hosting account or suspend access to your Services with or without notice.
If a customer’s hosting account is found to have violated the client content, excessive resource user policy and/or is storing files for archiving purposes, the contents will be removed and while we make best effort to contact customers before hand, can occur without notice.
Similarly Inodes are one of those things we rarely talk about unless their use becomes a problem. They’re fundamental bits of a file system that quietly do their job without any intervention from us.
What Is an Inode?
Inodes represent objects in the file system. Think of them as tiny index files. When you upload a file to your website (or to any disk or solid-state drive), the data that makes up the file is stored in multiple blocks. Those blocks aren’t always arranged in neat groups. They can be scattered across different areas of the disk. The inode contains instructions that let the file system know where to locate the data on the disk. It also includes some other information, or metadata, about the file.
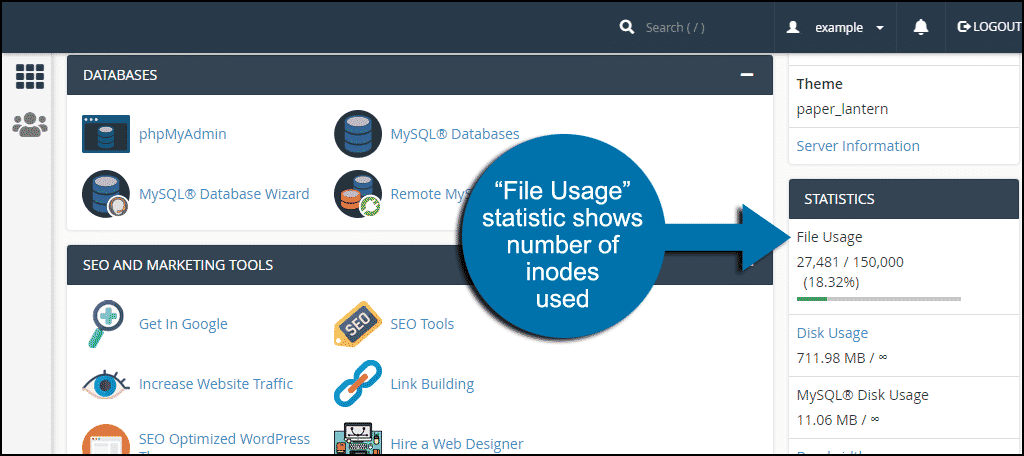
Where to See Your Inode Usage
You’ll notice the inode term is replaced with “File Usage.” That’s because they are essentially one of the same thing. We’ve just simplified the terms to make it easier for some of our customers.
If you need to know your current usage, you can:
You can see how many inodes your cPanel.
- Log in to cPanel.
- In the “Statistics” section in the right column, look for “File Usage.”
The first number is the number of inodes used. The second is your account’s inode quota.
When Can Inode Use Become a Problem?
The quick answer is because there are a limited number of inodes available in any file system. Every file on the system has a corresponding inode. A huge file uses a single inode in the file system, but a tiny file also uses one inode. A website that’s designed to generate or use many small files may not seem like a problem. After all, hundreds of thousands of tiny files take up very little storage space, right? They take up very little physical space, yes, but they consume a large number of inodes.
Inode Limitations Are in Place to Prevent Server Problems
Since the total number of inodes for the file system is limited, individual file system users (or web server users) have to be limited in how many they can create. If there were no limitations, a single user on the server could use all the available inodes while using relatively little storage space.
For the same reason, a hosting account may reach an inode limit before it reaches a storage space limit. To prevent a single user on a server from consuming all the available inodes, quotas are in place. Inode quotas aren’t specific to us. Every hosting provider imposes per-user inode use limits.
How to Reduce Inode Usage
The only way to reduce inode use is to reduce file use. When you delete a file, its inode is deleted as well. So here are a few ways to reduce your inode use.
- Delete Unused Files
The first way to reduce inode/file use is the simplest – delete unused files from your account. Some of the major culprits here are unused CMS installations. Many of us will install WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, or another CMS to give them a try. If we decide not to use them, we don’t always delete the installations. Most CMS packages contain hundreds—if not thousands—of files, so deleting them can reduce file use. As a bonus, older versions of CMS can be targets for hackers, so removing unused installations improves your website security. - Use Cloud File Storage
The second most effective method is to consider external file storage. Google, Amazon, and Microsoft all have cloud file storage systems, as do hundreds of other companies. If your site uses a lot of small files that can be stored on another server, such as images or documents, remote file storage can help lower your website file count. The difficulty in setting up a site to use remote file storage varies depending on how your website is configured, and whether you use a CMS. But the benefits can outweigh the setup costs. - Check Your Email
Finally, something that’s often overlooked when it comes to inode use is email. Your account’s inode quota includes all the files related to your account. That means not only website files, but email as well. If you can purge older email or large spam folders, etc., you can free up a lot of inode space.

